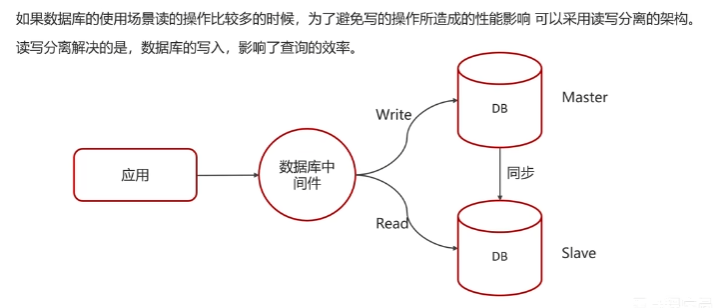
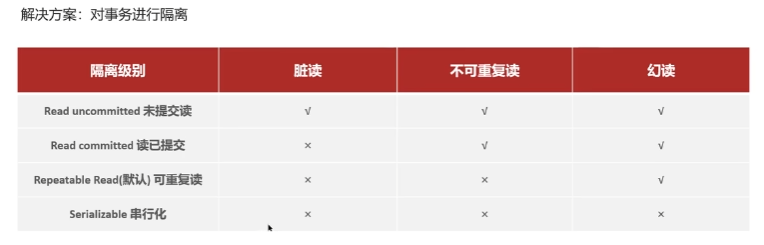
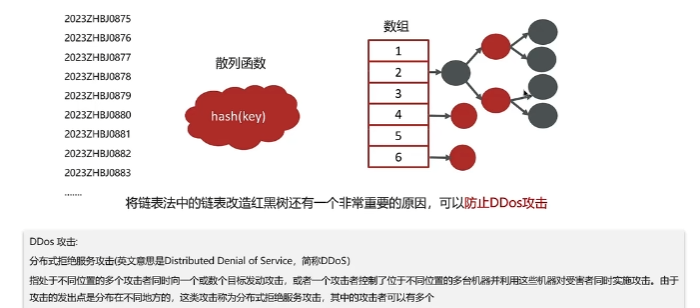
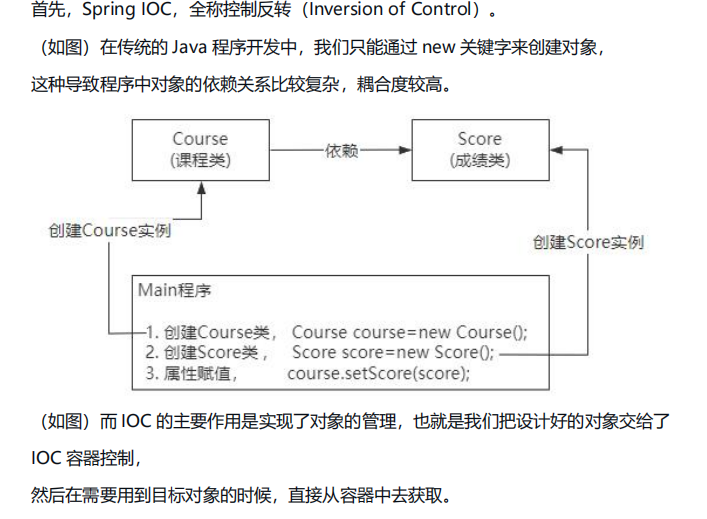
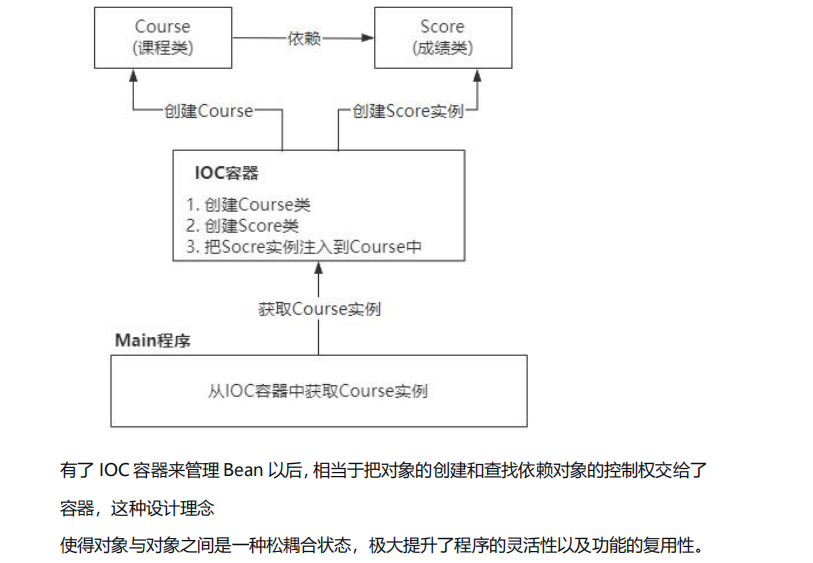
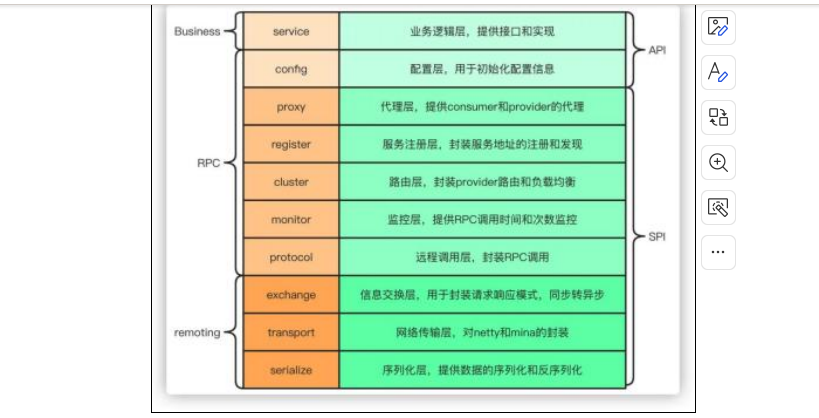
Redis 使用场景 缓存 缓存穿透
定义:查询一个不存在数据,每次查询都请求数据库
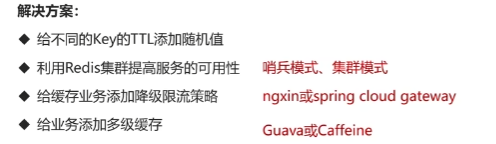
解决方案一:缓存空数据。
优点:简单
缺点:消耗内存,可能发生不一致问题
优点:内存占用少,没有多余key
缺点:实现复杂,存在误判
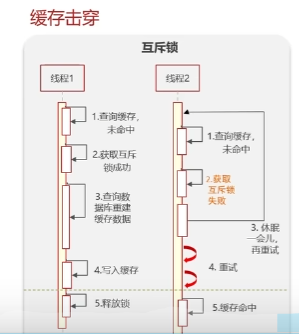
缓存击穿
定义:给某一个key设置了过期时间,当key过期的时候,恰好这个时间点对这个key有大量的并发请求过来,这些并发请求可能会瞬间把DB压垮。
解决方案一:互斥锁
可以保证数据强一致性,但是性能较差
性能较高,不能保证数据绝对一致。
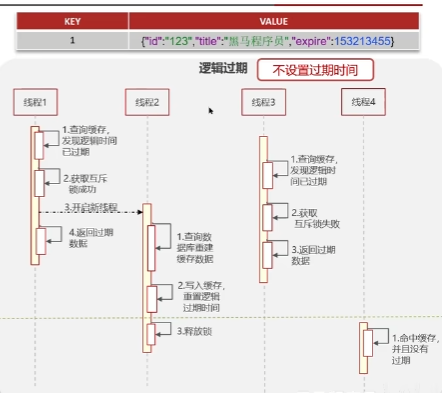
缓存雪崩
定义:同一时段大量的缓存key同时失效或者Redis服务宕机,导致大量请求到达数据库
双写一致性
一致性高:
读写锁效率更高一点。
一致性要求不高:
允许延时一致。
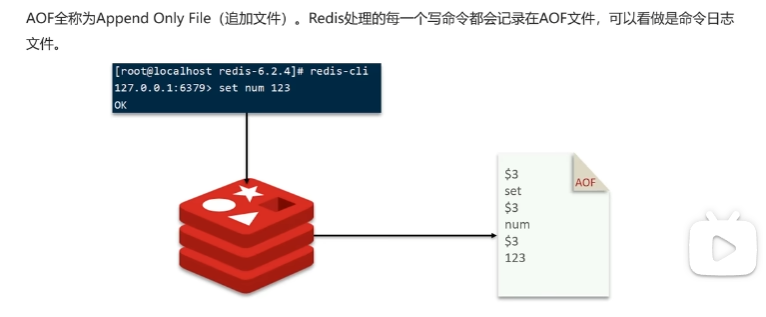
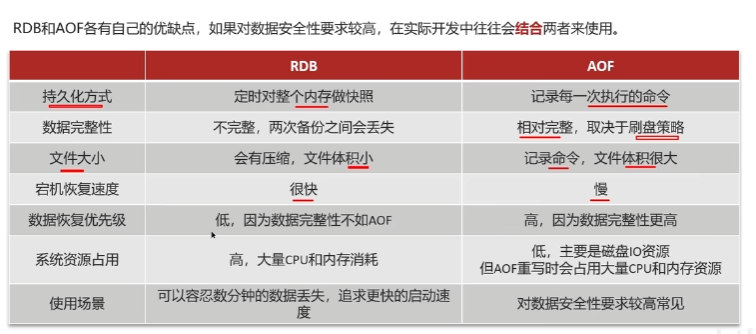
持久化
数据过期策略
Redis的过期策略是二者结合
数据淘汰策略
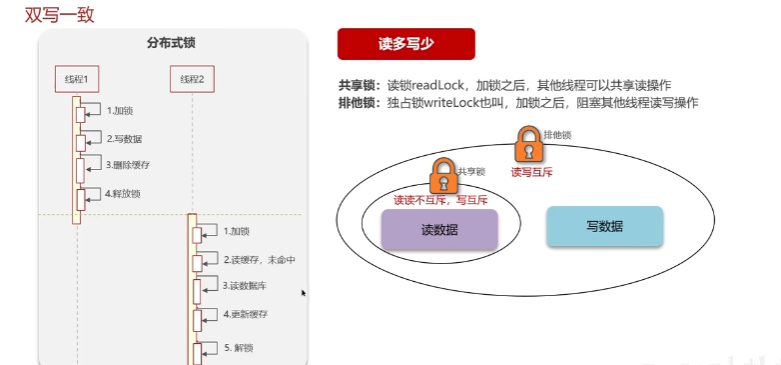
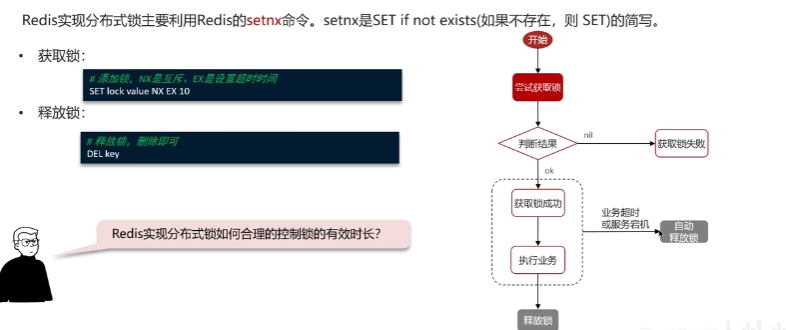
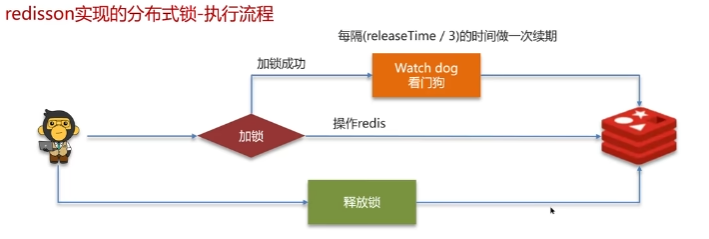
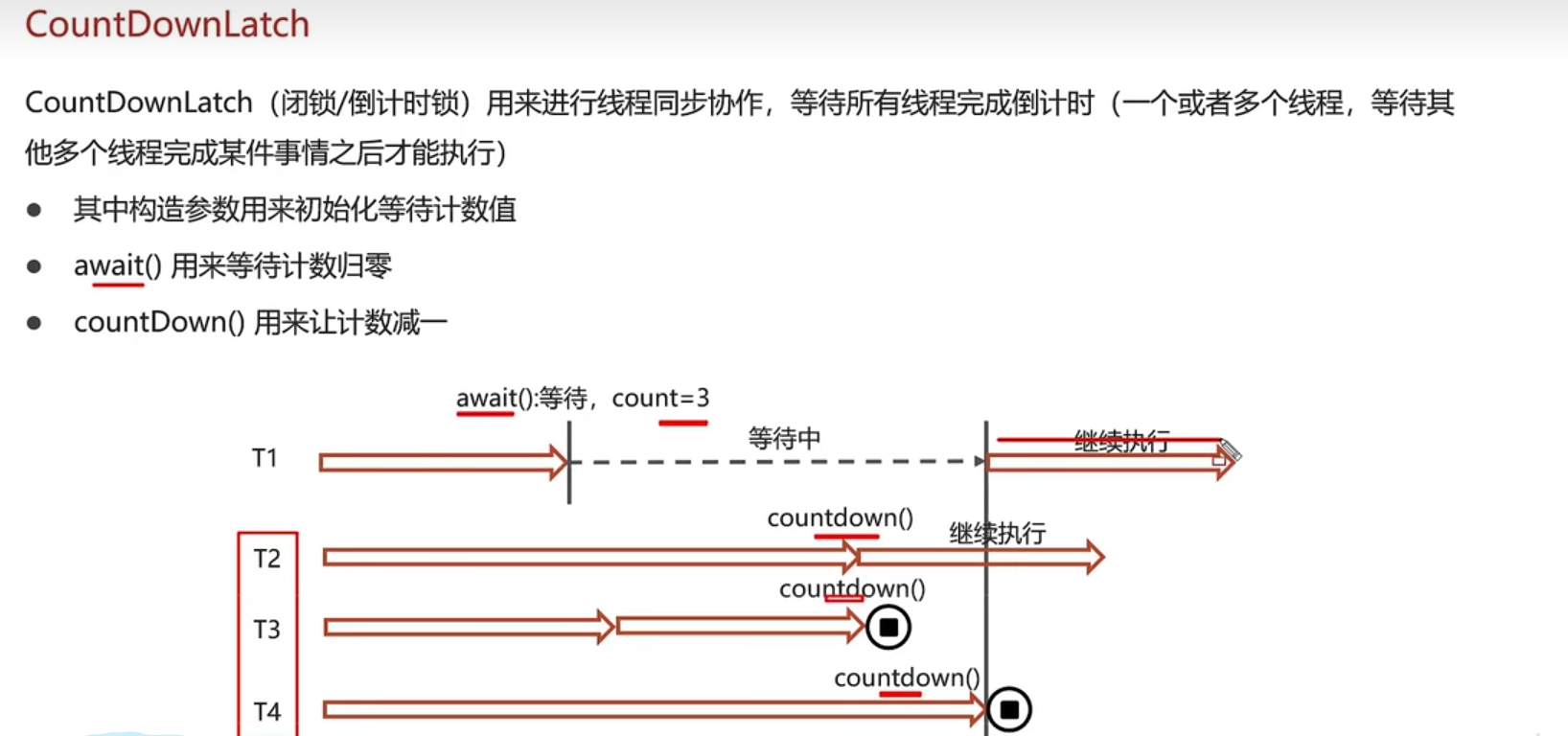
分布式锁
redisson实现的分布式锁-可重入。
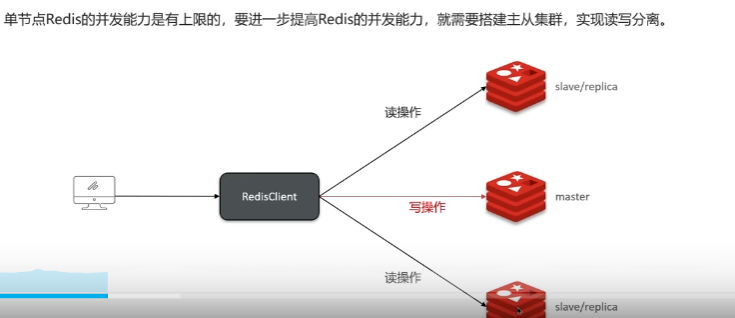
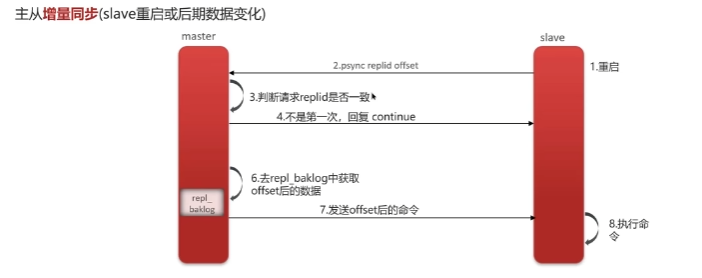
其他 Redis集群 主从复制
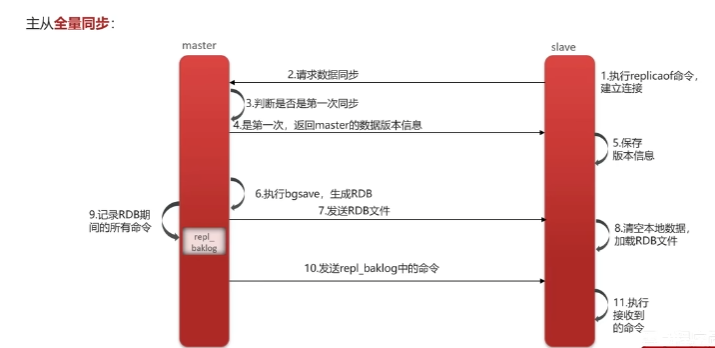
全量同步:
增量同步:
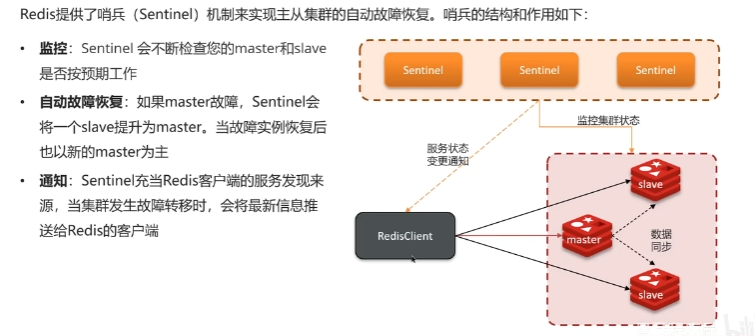
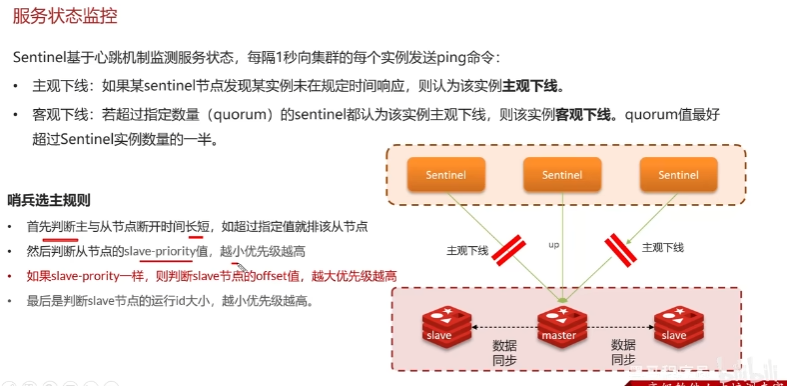
哨兵
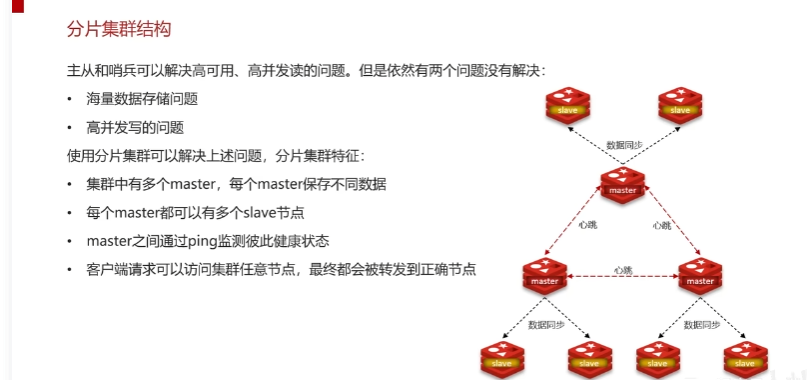
分片集群
其他
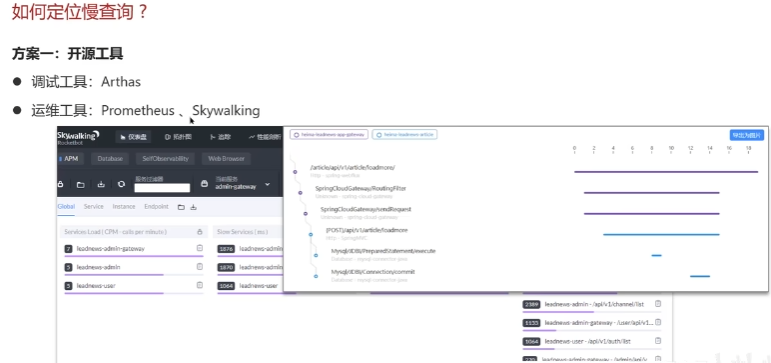
MYSQL 优化 定位慢查询
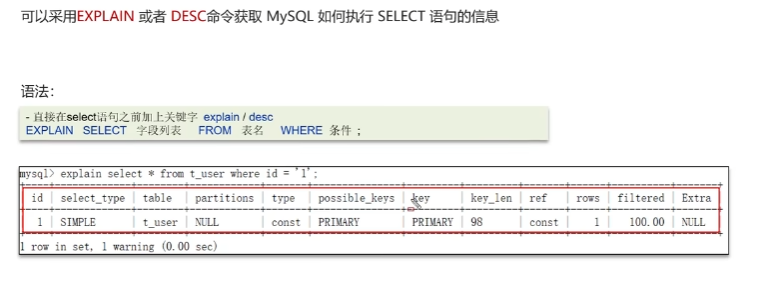
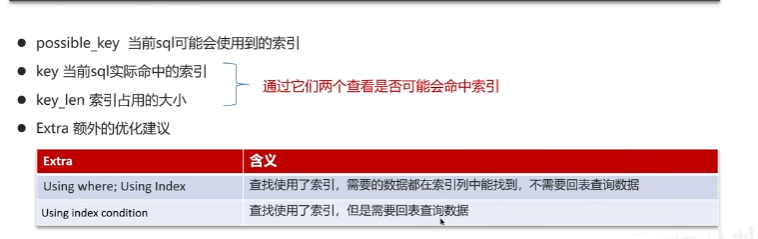
如何分析
索引
覆盖索引
超大分页
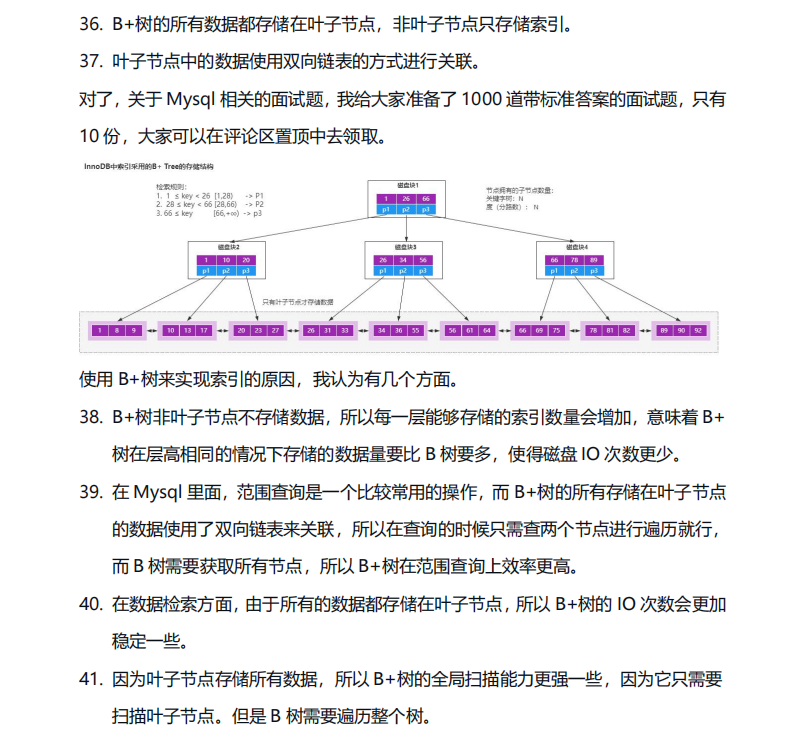
索引创建原则
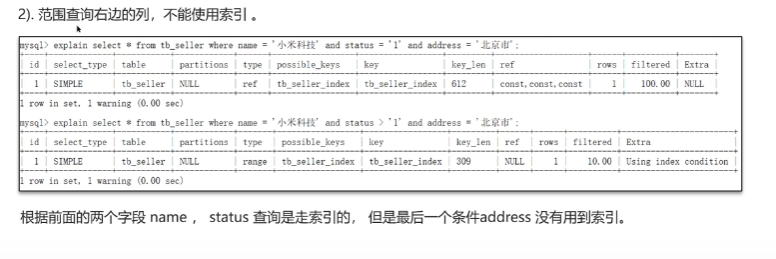
索引失效
经验
事务 特性
并发事务
解决方法
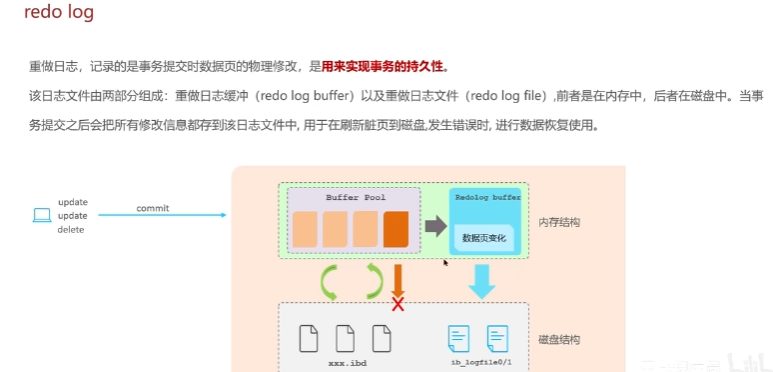
log
MVCC
主从同步原理
分库分表
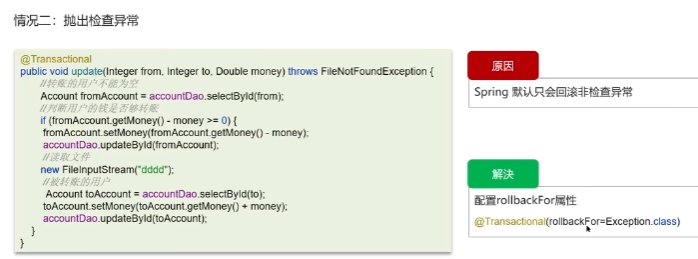
框架 Spring bean spring中的单例bean不是线程安全的。
AOP
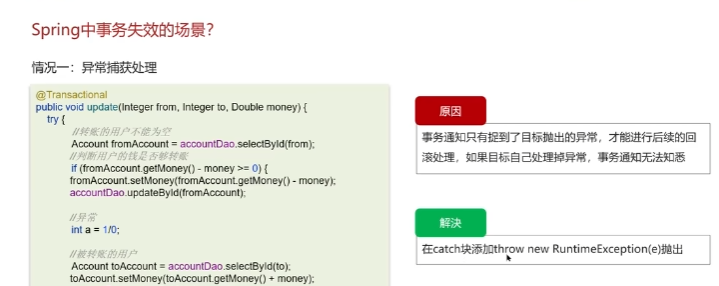
事务失效场景
bean的生命周期
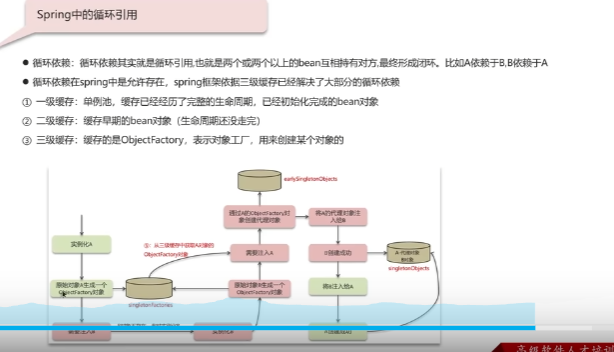
循环引用
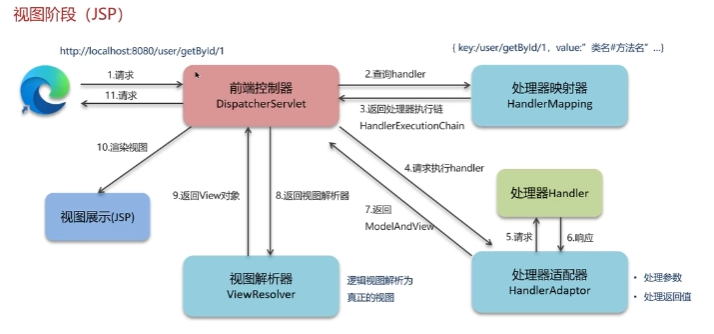
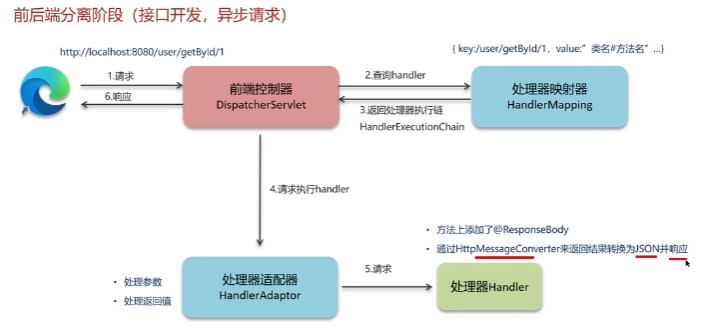
SpringMVC执行流程
Springboot自动配置原理 自动装配,简单来说就是自动把第三方组件的 Bean 装载到 Spring IOC 器里面,不需要开发人员再去写 Bean 的装配配置。
在 Spring Boot 应用里面,只需要在启动类加上@SpringBootApplication 注解就可以实现自动装配。
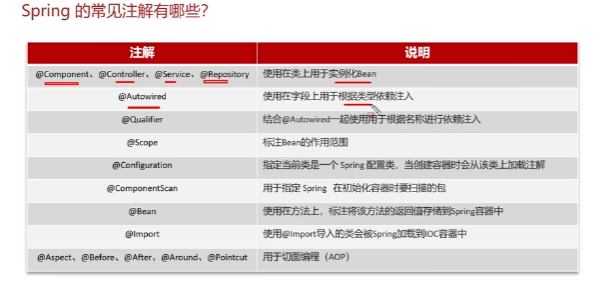
常见注解
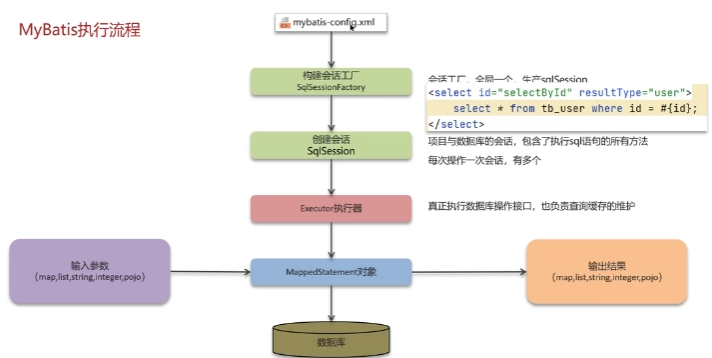
MyBatis 执行流程
延迟加载
一、二级缓存
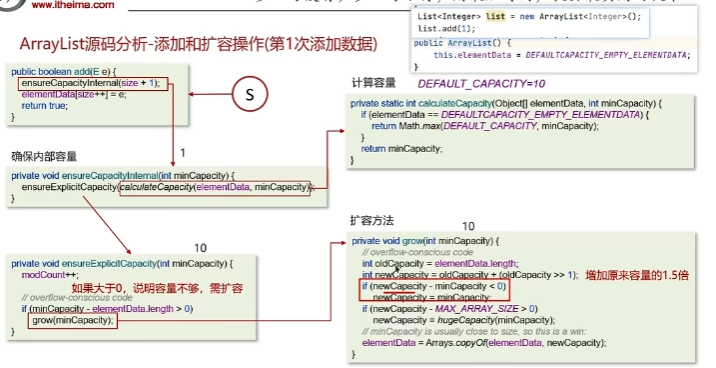
集合 List 数组 ArrayList源码
ArrayList底层原理
数组和List之间的转换
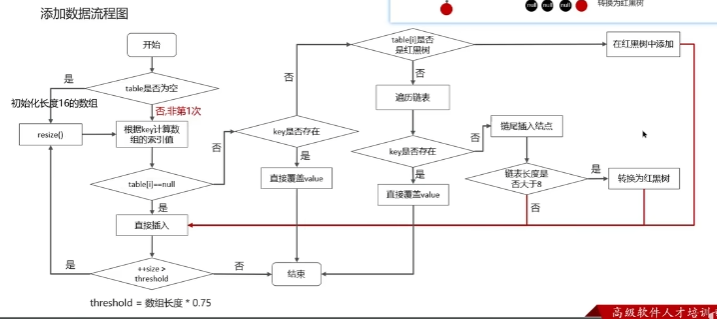
HashMap
实现原理
PUT
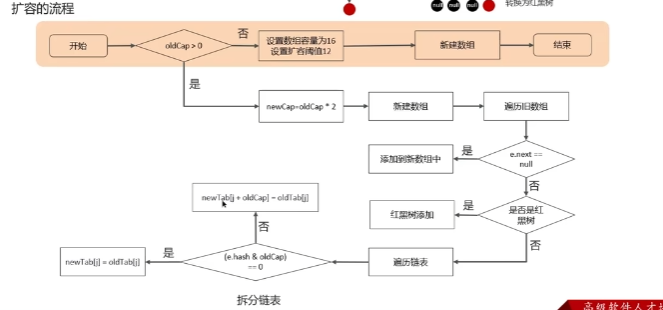
扩容机制
寻址算法
多线程 线程基础 进程和线程
创建线程方式
状态
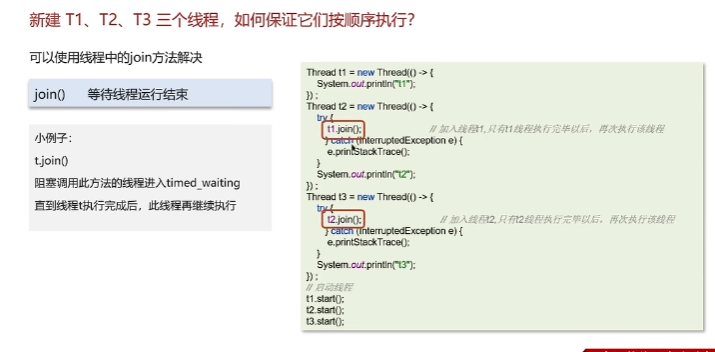
顺序执行
wait和sleep
如何终止线程
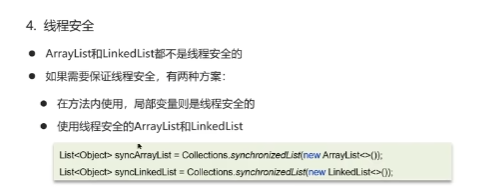
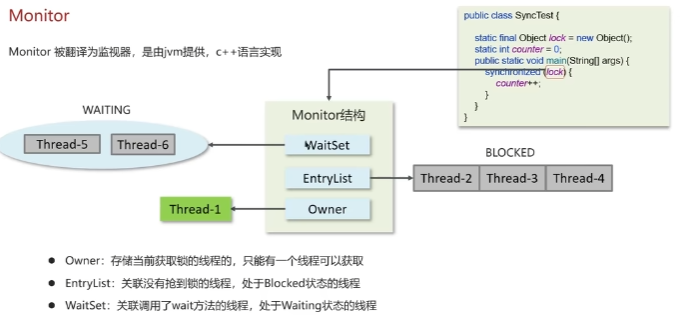
线程安全 synchronized底层原理
底层实现是Monitor
一旦锁发生竞争,都会升级为重量级锁。
JMM
CAS
volatile
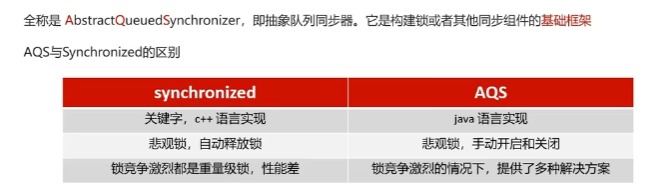
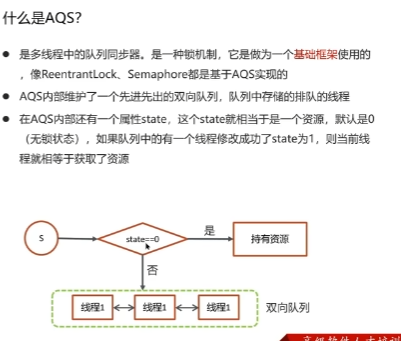
AQS
AQS核⼼思想是,如果被请求的共享资源空闲,则将当前请求资源的线程设置为有效的⼯作线程,并且将共享资源设置为锁定状态。如果被请求的共享资源被占⽤,那么就需要⼀套线程阻塞等待以及被唤醒时锁分配的机制,这个机制AQS是⽤CLH队列锁实现的,即将暂时获取不到锁的线程加⼊到队列中。
ReentrantLock
synchronized和Lock
死锁
ConcurrentHashMap
并发问题
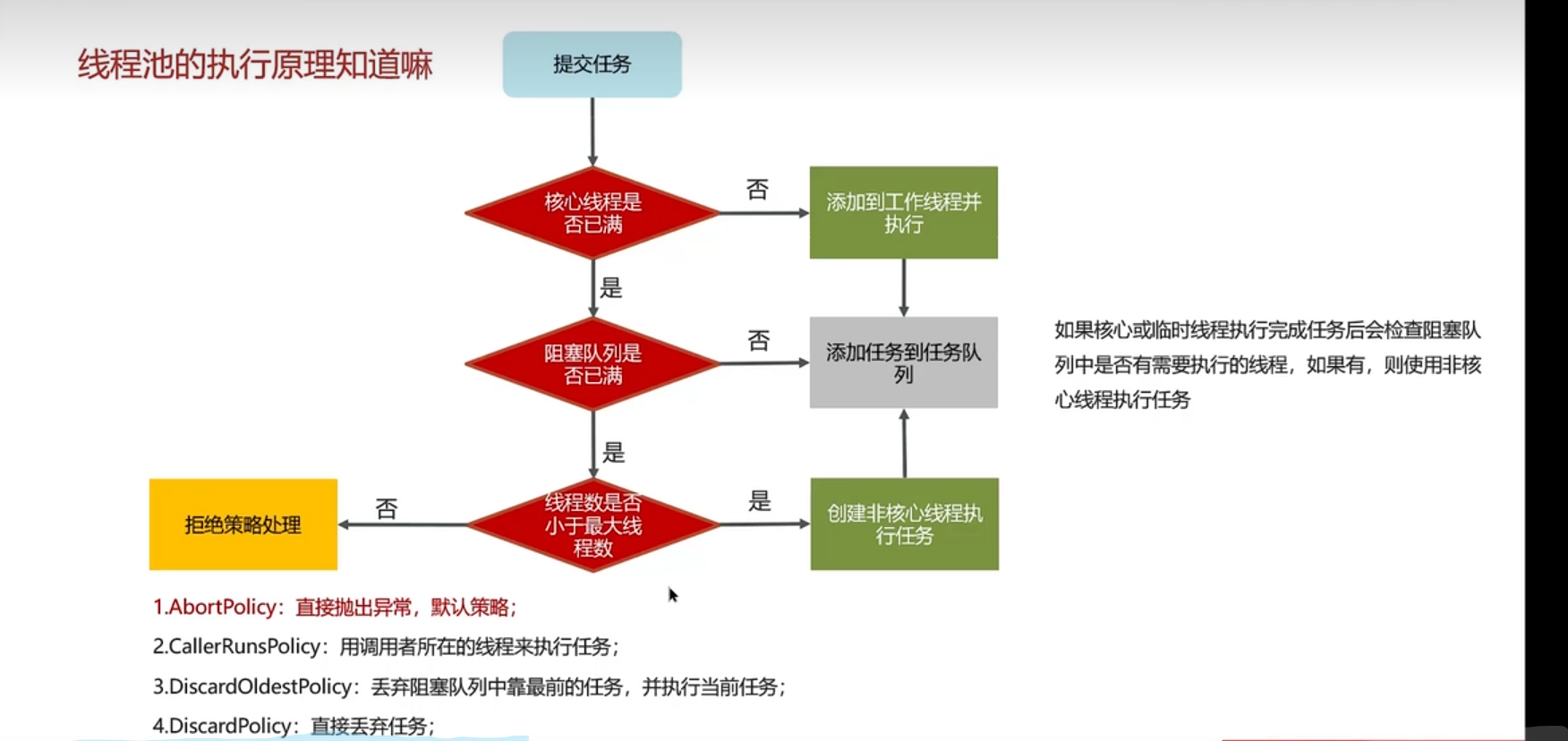
线程池 线程池核心参数
常见阻塞队列
如何缺点核心线程数
线程池种类
使用场景
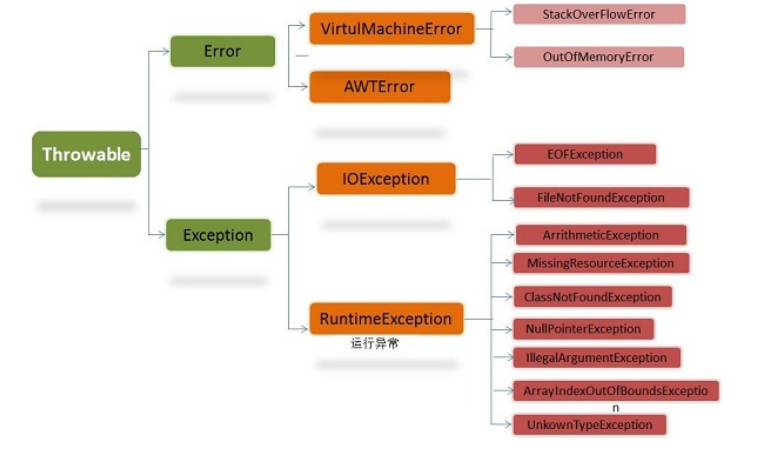
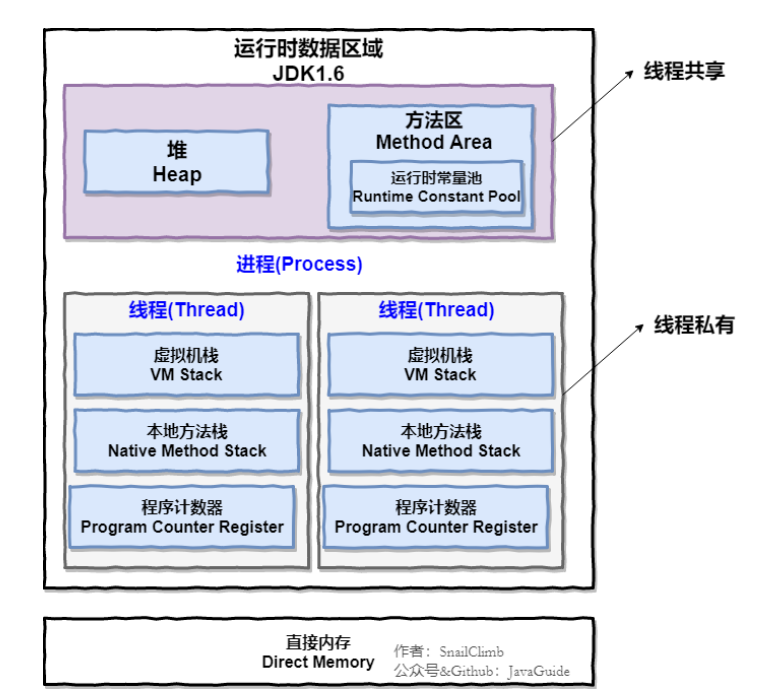
JVM JVM组成 程序计数器
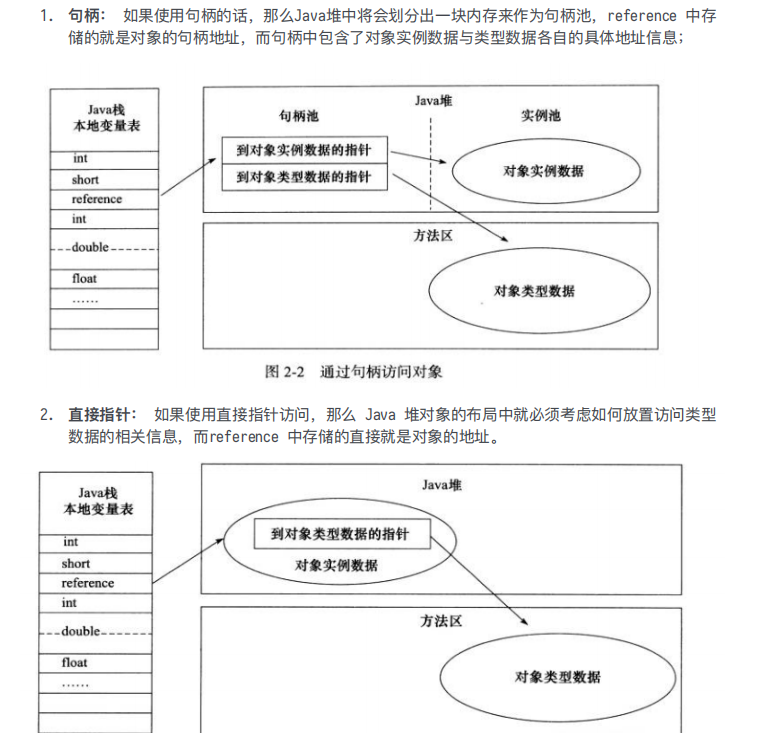
java堆
虚拟机栈
方法区
直接内存
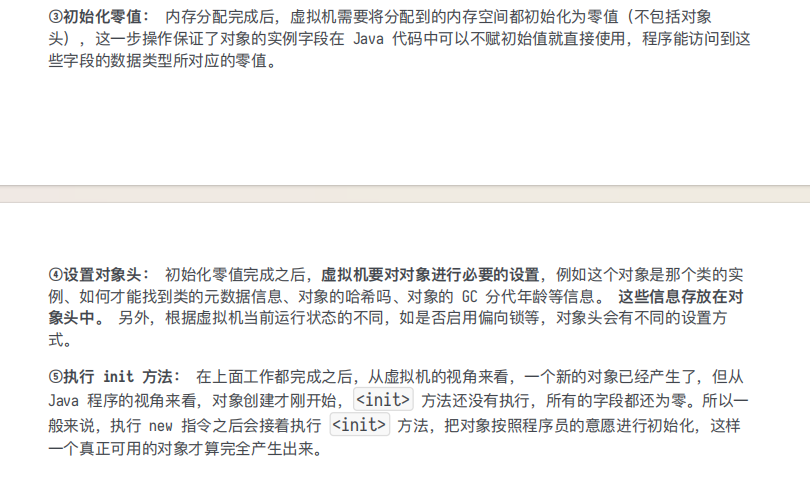
类装载过程
垃圾回收 何时回收
引用计数法可能会循环引用,造成泄露,所以现在经常用可达性分析。
垃圾回收算法
分代回收
引用
内存泄露排查思路
CPU排查思路
企业场景 设计模式 工厂设计模式
策略模式
责任链模式
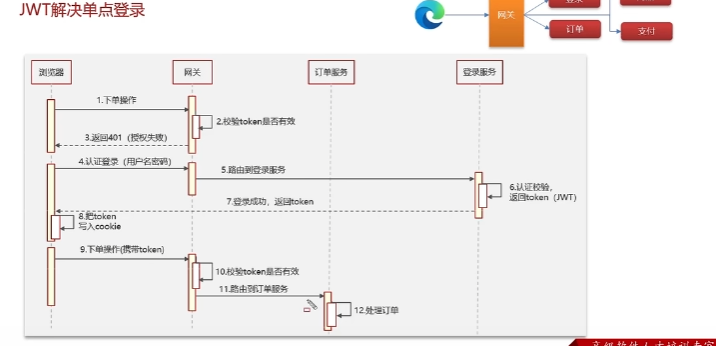
技术场景 单点登录
权限认证
上传数据安全性
棘手问题 采集日志 怎么快速定位系统瓶颈
补充1 基础
Java 序列化中如果有些字段不想进⾏序列化,怎么办?
对于不想进⾏序列化的变量,使⽤ transient 关键字修饰。
transient 关键字的作⽤是:阻⽌实例中那些⽤此关键字修饰的的变量序列化;当对象被反序列化时,被 transient 修饰的变量值不会被持久化和恢复。transient 只能修饰变量,不能修饰类和⽅法。
Java 中 IO 流
NIO :基于同步非阻塞 I/O 模型。尽管 NIO 支持非阻塞模式,但所有的 I/O 操作最终都是同步完成的。这意味着当一个 I/O 操作被发起时,它不会立即返回结果,而是需要应用程序通过轮询或选择器来检查操作是否完成。
AIO :真正的异步 I/O 模型。在 AIO 中,所有的 I/O 操作都是异步完成的。一旦发起一个 I/O 请求,该请求将立即返回,允许程序继续执行其他任务。操作系统会在 I/O 操作完成后通知应用程序。
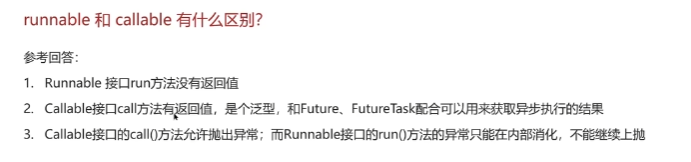
为什么我们调⽤ start() ⽅法时会执⾏run() ⽅法,为什么我们不能直接调⽤run() ⽅法
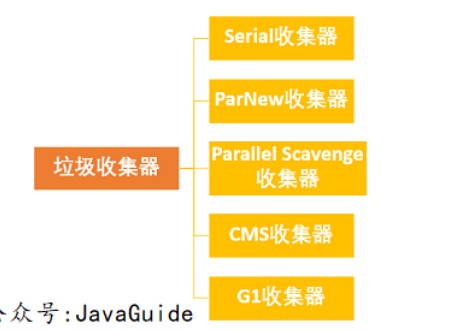
Serial收集器
Serial(串⾏)收集器收集器是最基本、历史最悠久的垃圾收集器了。⼤家看名字就知道这个收集器是⼀个单线程收集器了。它的 单线程 的意义不仅仅意味着它只会使⽤⼀条垃圾收集线程去完成垃圾收集⼯作,更重要的是它在进⾏垃圾收集⼯作的时候必须暂停其他所有的⼯作线程( “Stop The World” ),直到它收集结束。
ParNew收集器
ParNew收集器其实就是Serial收集器的多线程版本,除了使⽤多线程进⾏垃圾收集外,其余⾏为(控参数、收集算法、回收策略等等)和Serial收集器完全⼀样。
Parallel Scavenge收集器
⼀条SQL语句在MySQL中如何执⾏的
当 Dubbo 服务提供方出现故障导致 Zookeeper 剔除了这个服务的地址,
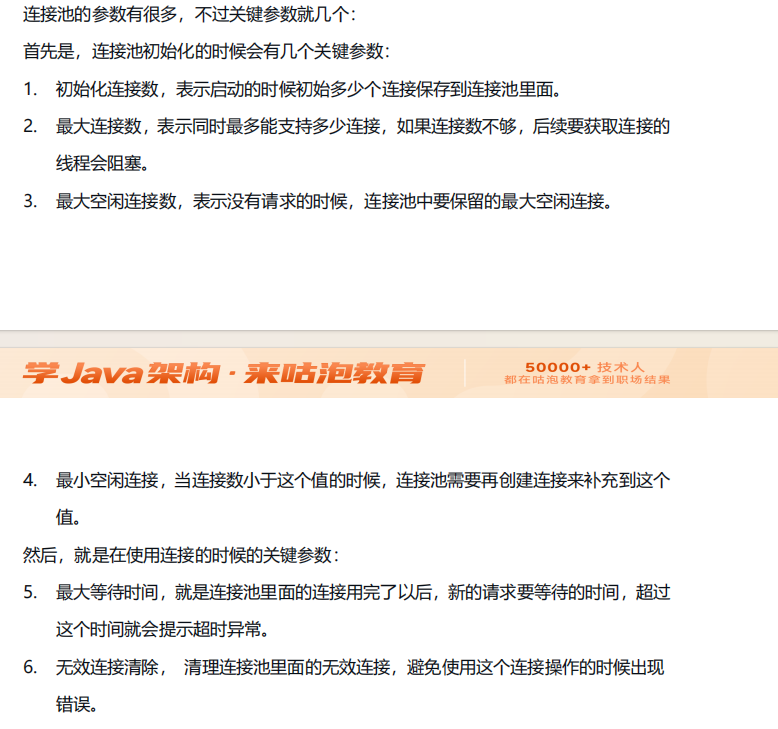
数据库连接池是一种池化技术,池化技术的核心思想是实现资源的复用,避免资源重复创建销毁的开销。
而在数据库的应用场景里面,应用程序每次向数据库发起 CRUD 操作的时候,都需要创建连接在数据库访问量较大的情况下,频繁的创建连接会带来较大的性能开销。
(如图)而连接池的核心思想,就是应用程序在启动的时候提前初始化一部分连接保存到连接池里面,当应用需要使用连接的时候,直接从连接池获取一个已经建立好的链接。连接池的设计,避免了每次连接的建立和释放带来的开销。
new String(“abc”)到底创建了几个对象?
String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder 区别
一个对象的GC年龄是储存在对象头里的,而对象头里有4位储存GC年龄,最大值为15。
两个 Integer 对象比较大小,为什么 100 等于 100,1000 不等于 1000
因为Intefer的valueOf方法,判断时如果目标值在-128-127则会直接从cache取值。
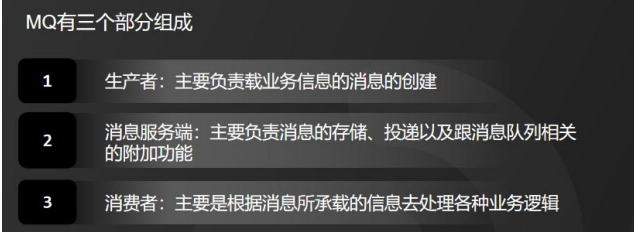
MQ 全称是 Message Queue,直译过来叫做消息队列,主要是作为分布式应用之间实现异步通信的方式。
主要由三个部分组成,分别是生产者、消息服务端和消费者
流量消峰
应用解耦
异步处理
给你 ab,ac,abc 字段,你是如何加索引 的
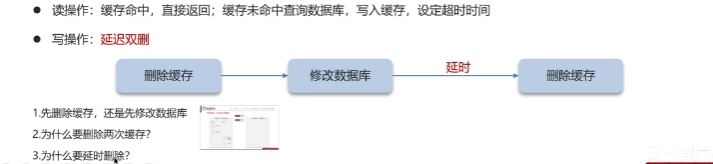
当应用程序需要去读取某个数据的时候,首先会先尝试去 Redis 里面加载,如果命中就直接返回。如果没有命中,就从数据库查询,查询到数据后再把这个数据缓存到 Redis里面。
在这种情况下,能够选择的方法只有几种。
先更新数据库,再更新缓存
先删除缓存,再更新数据库
如果先更新数据库,再更新缓存,如果缓存更新失败,就会导致数据库和 Redis 中的数据不一致。
如果是先删除缓存,再更新数据库,理想情况是应用下次访问 Redis 的时候,发现 Redis里面的数据是空的,就从数据库加载保存到 Redis 里面,那么数据是一致的。但是在极端情况下,由于删除 Redis 和更新数据库这两个操作并不是原子的,所以这个过程如果有其他线程来访问,还是会存在数据不一致问题。
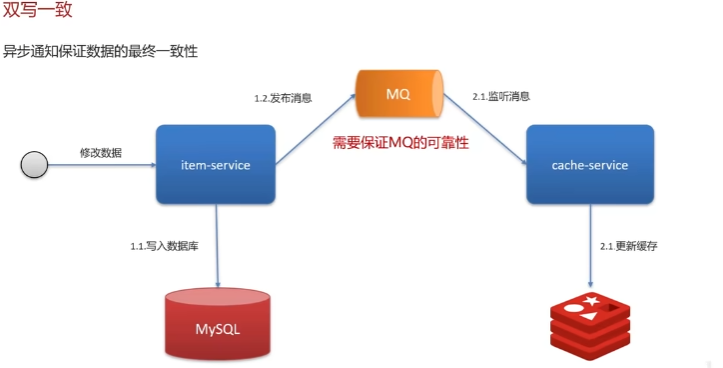
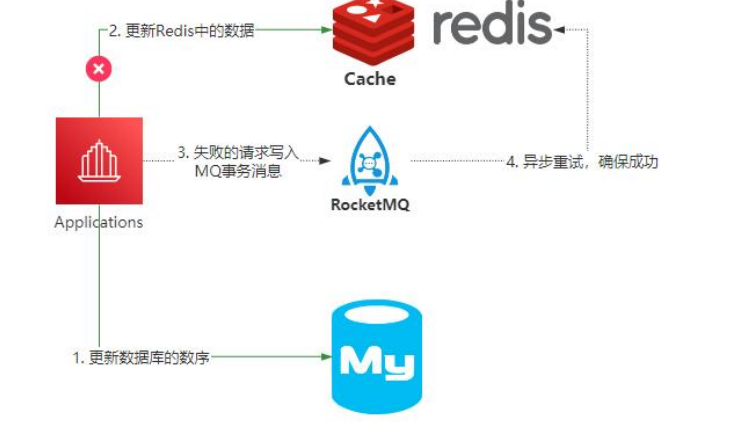
所以,如果需要在极端情况下仍然保证 Redis 和 Mysql 的数据一致性,就只能采用最终一致性方案。(如图)比如基于 RocketMQ 的可靠性消息通信,来实现最终一致性。
因为这里是基于最终一致性来实现的,如果业务场景不能接受数据的短期不一致性,那就不能使用这个方案来做。
RPC核心代码 基础 编写基于Vert.x实现的web服务器VertxHttpServer,能够监听指定端口并处理请求 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package com.yupi.yurpc.server; import io.vertx.core.Vertx; public class VertxHttpServer implements HttpServer { public void doStart(int port) { // 创建 Vert.x 实例 Vertx vertx = Vertx.vertx(); // 创建 HTTP 服务器 io.vertx.core.http.HttpServer server = vertx.createHttpServer(); // 监听端口并处理请求 server.requestHandler(request -> { // 处理 HTTP 请求 System.out.println("Received request: " + request.method() + " " + request.uri()); // 发送 HTTP 响应 request.response() .putHeader("content-type", "text/plain") .end("Hello from Vert.x HTTP server!"); }); // 启动 HTTP 服务器并监听指定端口 server.listen(port, result -> { if (result.succeeded()) { System.out.println("Server is now listening on port " + port); } else { System.err.println("Failed to start server: " + result.cause()); } }); } }
本地服务注册中心
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 package com.yupi.yurpc.registry; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /** * 本地注册中心 */ public class LocalRegistry { /** * 注册信息存储 */ private static final Map<String, Class<?>> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); /** * 注册服务 * * @param serviceName * @param implClass */ public static void register(String serviceName, Class<?> implClass) { map.put(serviceName, implClass); } /** * 获取服务 * * @param serviceName * @return */ public static Class<?> get(String serviceName) { return map.get(serviceName); } /** * 删除服务 * * @param serviceName */ public static void remove(String serviceName) { map.remove(serviceName); } }
请求处理器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 package com.yupi.yurpc.server; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcRequest; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcResponse; import com.yupi.yurpc.registry.LocalRegistry; import com.yupi.yurpc.serializer.JdkSerializer; import com.yupi.yurpc.serializer.Serializer; import io.vertx.core.Handler; import io.vertx.core.buffer.Buffer; import io.vertx.core.http.HttpServerRequest; import io.vertx.core.http.HttpServerResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; /** * HTTP 请求处理 */ public class HttpServerHandler implements Handler<HttpServerRequest> { @Override public void handle(HttpServerRequest request) { // 指定序列化器 final Serializer serializer = new JdkSerializer(); // 记录日志 System.out.println("Received request: " + request.method() + " " + request.uri()); // 异步处理 HTTP 请求 request.bodyHandler(body -> { byte[] bytes = body.getBytes(); RpcRequest rpcRequest = null; try { rpcRequest = serializer.deserialize(bytes, RpcRequest.class); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 构造响应结果对象 RpcResponse rpcResponse = new RpcResponse(); // 如果请求为 null,直接返回 if (rpcRequest == null) { rpcResponse.setMessage("rpcRequest is null"); doResponse(request, rpcResponse, serializer); return; } try { // 获取要调用的服务实现类,通过反射调用 Class<?> implClass = LocalRegistry.get(rpcRequest.getServiceName()); Method method = implClass.getMethod(rpcRequest.getMethodName(), rpcRequest.getParameterTypes()); Object result = method.invoke(implClass.newInstance(), rpcRequest.getArgs()); // 封装返回结果 rpcResponse.setData(result); rpcResponse.setDataType(method.getReturnType()); rpcResponse.setMessage("ok"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); rpcResponse.setMessage(e.getMessage()); rpcResponse.setException(e); } // 响应 doResponse(request, rpcResponse, serializer); }); } /** * 响应 * * @param request * @param rpcResponse * @param serializer */ void doResponse(HttpServerRequest request, RpcResponse rpcResponse, Serializer serializer) { HttpServerResponse httpServerResponse = request.response() .putHeader("content-type", "application/json"); try { // 序列化 byte[] serialized = serializer.serialize(rpcResponse); httpServerResponse.end(Buffer.buffer(serialized)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); httpServerResponse.end(Buffer.buffer()); } } }
TCP版本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 package com.yupi.yurpc.server.tcp; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcRequest; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcResponse; import com.yupi.yurpc.protocol.ProtocolMessage; import com.yupi.yurpc.protocol.ProtocolMessageDecoder; import com.yupi.yurpc.protocol.ProtocolMessageEncoder; import com.yupi.yurpc.protocol.ProtocolMessageTypeEnum; import com.yupi.yurpc.registry.LocalRegistry; import io.vertx.core.Handler; import io.vertx.core.buffer.Buffer; import io.vertx.core.net.NetSocket; import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class TcpServerHandler implements Handler<NetSocket> { @Override public void handle(NetSocket netSocket) { // 处理连接 netSocket.handler(buffer -> { // 接受请求,解码 ProtocolMessage<RpcRequest> protocolMessage; try { protocolMessage = (ProtocolMessage<RpcRequest>) ProtocolMessageDecoder.decode(buffer); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException("协议消息解码错误"); } RpcRequest rpcRequest = protocolMessage.getBody(); // 处理请求 // 构造响应结果对象 RpcResponse rpcResponse = new RpcResponse(); try { // 获取要调用的服务实现类,通过反射调用 Class<?> implClass = LocalRegistry.get(rpcRequest.getServiceName()); Method method = implClass.getMethod(rpcRequest.getMethodName(), rpcRequest.getParameterTypes()); Object result = method.invoke(implClass.newInstance(), rpcRequest.getArgs()); // 封装返回结果 rpcResponse.setData(result); rpcResponse.setDataType(method.getReturnType()); rpcResponse.setMessage("ok"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); rpcResponse.setMessage(e.getMessage()); rpcResponse.setException(e); } // 发送响应,编码 ProtocolMessage.Header header = protocolMessage.getHeader(); header.setType((byte) ProtocolMessageTypeEnum.RESPONSE.getKey()); ProtocolMessage<RpcResponse> responseProtocolMessage = new ProtocolMessage<>(header, rpcResponse); try { Buffer encode = ProtocolMessageEncoder.encode(responseProtocolMessage); netSocket.write(encode); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException("协议消息编码错误"); } }); } }
请求发送 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 package com.yupi.yurpc.proxy; import cn.hutool.core.collection.CollUtil; import cn.hutool.core.util.IdUtil; import cn.hutool.http.HttpRequest; import cn.hutool.http.HttpResponse; import com.yupi.yurpc.RpcApplication; import com.yupi.yurpc.config.RpcConfig; import com.yupi.yurpc.constant.RpcConstant; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcRequest; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcResponse; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.ServiceMetaInfo; import com.yupi.yurpc.protocol.*; import com.yupi.yurpc.registry.Registry; import com.yupi.yurpc.registry.RegistryFactory; import com.yupi.yurpc.serializer.Serializer; import com.yupi.yurpc.serializer.SerializerFactory; import io.vertx.core.Future; import io.vertx.core.Vertx; import io.vertx.core.buffer.Buffer; import io.vertx.core.net.NetClient; import io.vertx.core.net.NetSocket; import io.vertx.core.net.SocketAddress; import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; /** * 服务代理(JDK 动态代理) * * @author <a href="https://github.com/liyupi">程序员鱼皮</a> * @learn <a href="https://codefather.cn">编程宝典</a> * @from <a href="https://yupi.icu">编程导航知识星球</a> */ public class ServiceProxy implements InvocationHandler { /** * 调用代理 * * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { // 指定序列化器 final Serializer serializer = SerializerFactory.getInstance(RpcApplication.getRpcConfig().getSerializer()); // 构造请求 String serviceName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName(); RpcRequest rpcRequest = RpcRequest.builder() .serviceName(serviceName) .methodName(method.getName()) .parameterTypes(method.getParameterTypes()) .args(args) .build(); try { // 序列化 byte[] bodyBytes = serializer.serialize(rpcRequest); // 从注册中心获取服务提供者请求地址 RpcConfig rpcConfig = RpcApplication.getRpcConfig(); Registry registry = RegistryFactory.getInstance(rpcConfig.getRegistryConfig().getRegistry()); ServiceMetaInfo serviceMetaInfo = new ServiceMetaInfo(); serviceMetaInfo.setServiceName(serviceName); serviceMetaInfo.setServiceVersion(RpcConstant.DEFAULT_SERVICE_VERSION); List<ServiceMetaInfo> serviceMetaInfoList = registry.serviceDiscovery(serviceMetaInfo.getServiceKey()); if (CollUtil.isEmpty(serviceMetaInfoList)) { throw new RuntimeException("暂无服务地址"); } ServiceMetaInfo selectedServiceMetaInfo = serviceMetaInfoList.get(0); // 发送 TCP 请求 Vertx vertx = Vertx.vertx(); NetClient netClient = vertx.createNetClient(); CompletableFuture<RpcResponse> responseFuture = new CompletableFuture<>(); netClient.connect(selectedServiceMetaInfo.getServicePort(), selectedServiceMetaInfo.getServiceHost(), result -> { if (result.succeeded()) { System.out.println("Connected to TCP server"); io.vertx.core.net.NetSocket socket = result.result(); // 发送数据 // 构造消息 ProtocolMessage<RpcRequest> protocolMessage = new ProtocolMessage<>(); ProtocolMessage.Header header = new ProtocolMessage.Header(); header.setMagic(ProtocolConstant.PROTOCOL_MAGIC); header.setVersion(ProtocolConstant.PROTOCOL_VERSION); header.setSerializer((byte) ProtocolMessageSerializerEnum.getEnumByValue(RpcApplication.getRpcConfig().getSerializer()).getKey()); header.setType((byte) ProtocolMessageTypeEnum.REQUEST.getKey()); header.setRequestId(IdUtil.getSnowflakeNextId()); protocolMessage.setHeader(header); protocolMessage.setBody(rpcRequest); // 编码请求 try { Buffer encodeBuffer = ProtocolMessageEncoder.encode(protocolMessage); socket.write(encodeBuffer); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException("协议消息编码错误"); } // 接收响应 socket.handler(buffer -> { try { ProtocolMessage<RpcResponse> rpcResponseProtocolMessage = (ProtocolMessage<RpcResponse>) ProtocolMessageDecoder.decode(buffer); responseFuture.complete(rpcResponseProtocolMessage.getBody()); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException("协议消息解码错误"); } }); } else { System.err.println("Failed to connect to TCP server"); } }); RpcResponse rpcResponse = responseFuture.get(); // 记得关闭连接 netClient.close(); return rpcResponse.getData(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
序列化器 序列化器JSON JSON序列化器需要考虑对象转换的兼容问题,主要是因为Java语言中的泛型擦除(Type Erasure)机制和JSON数据格式本身的特性。
泛型擦除 : 在Java中,泛型信息在编译后会被擦除,这意味着运行时无法直接获取泛型参数的具体类型信息。例如,List<String> 和 List<Integer> 在运行时都被视为 List 类型。当使用Jackson等库进行反序列化时,默认情况下它们可能不知道如何将JSON对象映射回原始的Java泛型类型,可能会默认返回如 LinkedHashMap 这样的类型。JSON与Java对象模型差异 : JSON是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,它没有像Java那样的复杂类型系统。JSON只支持几种基本类型(字符串、数字、布尔值、数组、对象和null)。因此,当从JSON反序列化到Java对象时,有时候JSON结构并不能完全对应Java类的结构,特别是对于复杂的嵌套对象或自定义类型。
Kryo 是一个专门为Java设计的高效序列化框架,它与JSON序列化器如Jackson相比,在处理对象转换兼容性问题上有不同的特性,这使得Kryo在某些情况下不需要特别考虑类型转换的兼容问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 package com.yupi.yurpc.serializer; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcRequest; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcResponse; import java.io.IOException; public class JsonSerializer implements Serializer { private static final ObjectMapper OBJECT_MAPPER = new ObjectMapper(); @Override public <T> byte[] serialize(T obj) throws IOException { return OBJECT_MAPPER.writeValueAsBytes(obj); } @Override public <T> T deserialize(byte[] bytes, Class<T> classType) throws IOException { T obj = OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(bytes, classType); if (obj instanceof RpcRequest) { return handleRequest((RpcRequest) obj, classType); } if (obj instanceof RpcResponse) { return handleResponse((RpcResponse) obj, classType); } return obj; } /** * 由于 Object 的原始对象会被擦除,导致反序列化时会被作为 LinkedHashMap 无法转换成原始对象,因此这里做了特殊处理 * * @param rpcRequest rpc 请求 * @param type 类型 * @return {@link T} * @throws IOException IO异常 */ private <T> T handleRequest(RpcRequest rpcRequest, Class<T> type) throws IOException { Class<?>[] parameterTypes = rpcRequest.getParameterTypes(); Object[] args = rpcRequest.getArgs(); // 循环处理每个参数的类型 for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) { Class<?> clazz = parameterTypes[i]; // 如果类型不同,则重新处理一下类型 if (!clazz.isAssignableFrom(args[i].getClass())) { byte[] argBytes = OBJECT_MAPPER.writeValueAsBytes(args[i]); args[i] = OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(argBytes, clazz); } } return type.cast(rpcRequest); } /** * 由于 Object 的原始对象会被擦除,导致反序列化时会被作为 LinkedHashMap 无法转换成原始对象,因此这里做了特殊处理 * * @param rpcResponse rpc 响应 * @param type 类型 * @return {@link T} * @throws IOException IO异常 */ private <T> T handleResponse(RpcResponse rpcResponse, Class<T> type) throws IOException { // 处理响应数据 byte[] dataBytes = OBJECT_MAPPER.writeValueAsBytes(rpcResponse.getData()); rpcResponse.setData(OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(dataBytes, rpcResponse.getDataType())); return type.cast(rpcResponse); } }
kryo序列器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 package com.yupi.yurpc.serializer; import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.Kryo; import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.io.Input; import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.io.Output; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; /** * Kryo 序列化器 * * @author <a href="https://github.com/liyupi">程序员鱼皮</a> * @learn <a href="https://codefather.cn">编程宝典</a> * @from <a href="https://yupi.icu">编程导航知识星球</a> */ public class KryoSerializer implements Serializer { /** * kryo 线程不安全,使用 ThreadLocal 保证每个线程只有一个 Kryo */ private static final ThreadLocal<Kryo> KRYO_THREAD_LOCAL = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> { Kryo kryo = new Kryo(); // 设置动态动态序列化和反序列化类,不提前注册所有类(可能有安全问题) kryo.setRegistrationRequired(false); return kryo; }); @Override public <T> byte[] serialize(T obj) { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); Output output = new Output(byteArrayOutputStream); KRYO_THREAD_LOCAL.get().writeObject(output, obj); output.close(); return byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); } @Override public <T> T deserialize(byte[] bytes, Class<T> classType) { ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes); Input input = new Input(byteArrayInputStream); T result = KRYO_THREAD_LOCAL.get().readObject(input, classType); input.close(); return result; } }
hessian 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package com.yupi.yurpc.serializer; import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianInput; import com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianOutput; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; /** * Hessian 序列化器 * * @author <a href="https://github.com/liyupi">程序员鱼皮</a> * @learn <a href="https://codefather.cn">编程宝典</a> * @from <a href="https://yupi.icu">编程导航知识星球</a> */ public class HessianSerializer implements Serializer { @Override public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) throws IOException { ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); HessianOutput ho = new HessianOutput(bos); ho.writeObject(object); return bos.toByteArray(); } @Override public <T> T deserialize(byte[] bytes, Class<T> tClass) throws IOException { ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes); HessianInput hi = new HessianInput(bis); return (T) hi.readObject(tClass); } }
注册中心
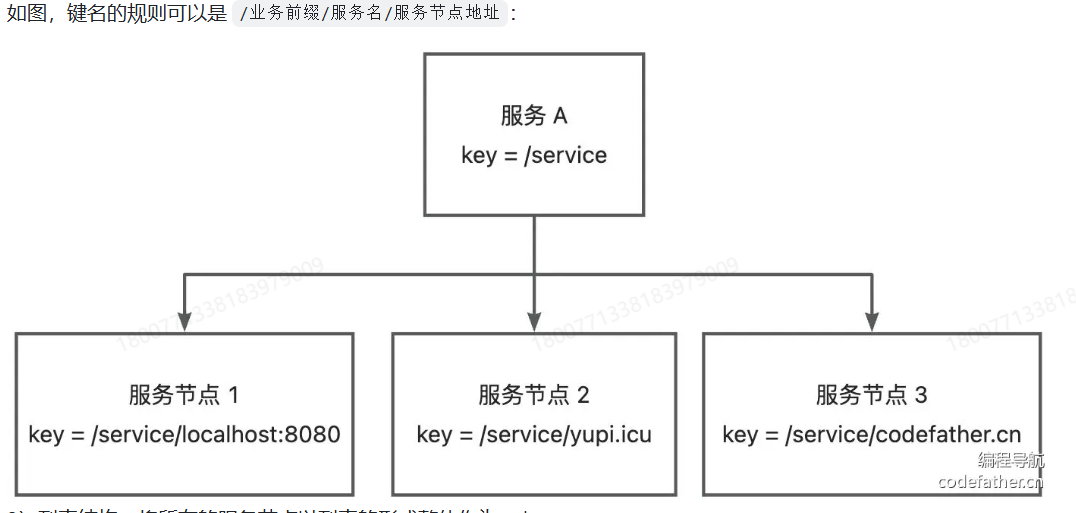
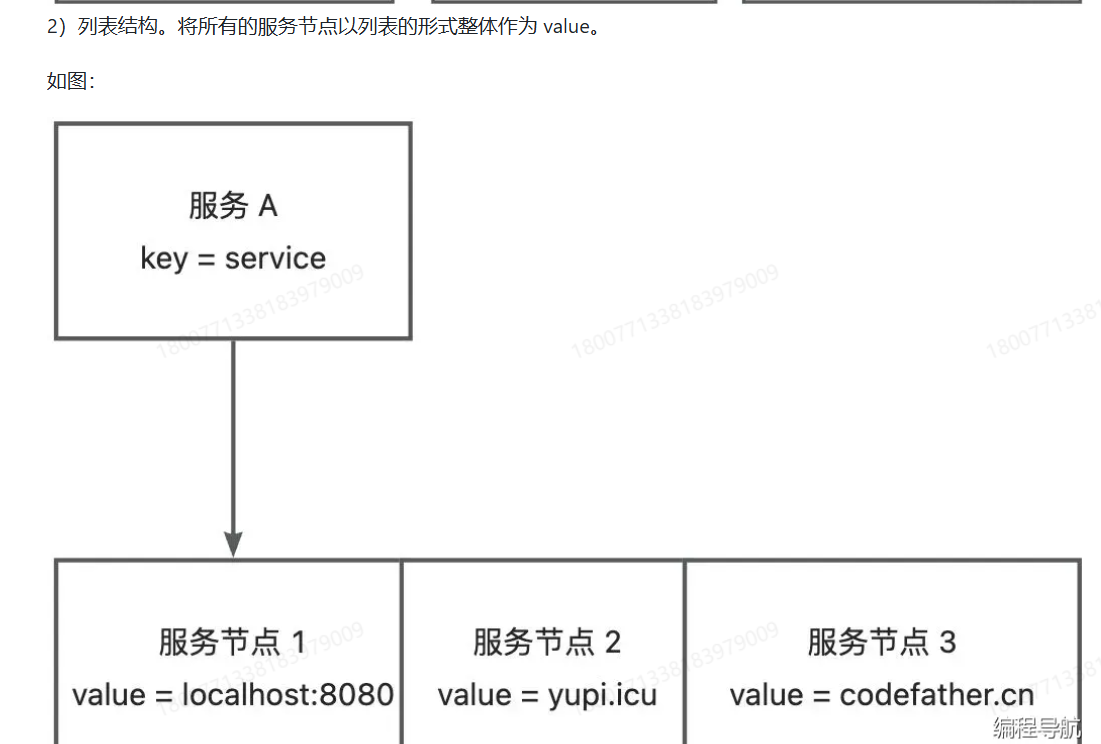
对于ZooKeeper和Etcd这种支持层级查询的中间件,用第一种更加清晰。
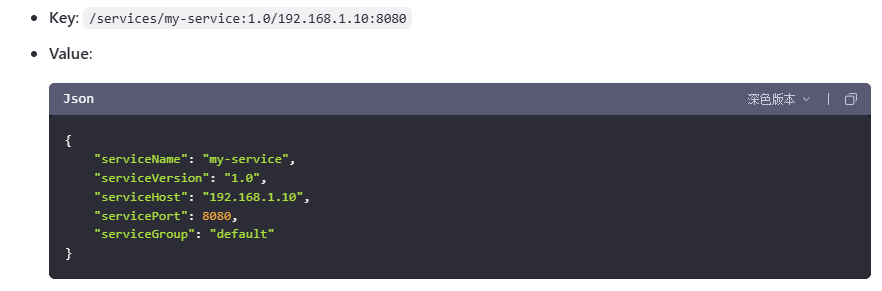
注册信息定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package com.yupi.yurpc.model; /** * 服务元信息(注册信息) */ public class ServiceMetaInfo { /** * 服务名称 */ private String serviceName; /** * 服务版本号 */ private String serviceVersion = "1.0"; /** * 服务域名 */ private String serviceHost; /** * 服务端口号 */ private Integer servicePort; /** * 服务分组(暂未实现) */ private String serviceGroup = "default"; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 /** * 获取服务键名 * * @return */ public String getServiceKey() { // 后续可扩展服务分组 // return String.format("%s:%s:%s", serviceName, serviceVersion, serviceGroup); return String.format("%s:%s", serviceName, serviceVersion); } /** * 获取服务注册节点键名 * * @return */ public String getServiceNodeKey() { return String.format("%s/%s:%s", getServiceKey(), serviceHost, servicePort); }
注册 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public void register(ServiceMetaInfo serviceMetaInfo) throws Exception { // 创建 Lease 和 KV 客户端 Lease leaseClient = client.getLeaseClient(); // 创建一个 30 秒的租约 long leaseId = leaseClient.grant(30).get().getID(); // 设置要存储的键值对 String registerKey = ETCD_ROOT_PATH + serviceMetaInfo.getServiceNodeKey(); ByteSequence key = ByteSequence.from(registerKey, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); ByteSequence value = ByteSequence.from(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(serviceMetaInfo), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // 将键值对与租约关联起来,并设置过期时间 PutOption putOption = PutOption.builder().withLeaseId(leaseId).build(); kvClient.put(key, value, putOption).get(); }
假设有一个服务实例:
serviceNameserviceVersionserviceHostservicePort
服务发现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public List<ServiceMetaInfo> serviceDiscovery(String serviceKey) { // 前缀搜索,结尾一定要加 '/' String searchPrefix = ETCD_ROOT_PATH + serviceKey + "/"; try { // 前缀查询 GetOption getOption = GetOption.builder().isPrefix(true).build(); List<KeyValue> keyValues = kvClient.get( ByteSequence.from(searchPrefix, StandardCharsets.UTF_8), getOption) .get() .getKvs(); // 解析服务信息 return keyValues.stream() .map(keyValue -> { String value = keyValue.getValue().toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); return JSONUtil.toBean(value, ServiceMetaInfo.class); }) .collect(Collectors.toList()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException("获取服务列表失败", e); } }
这段代码实现了基于 etcd 的服务发现功能,具体步骤如下:
构建查询前缀 :根据给定的服务键构建一个特定的路径前缀。配置查询选项 :设置查询条件为前缀匹配。执行查询 :向 etcd 发起查询请求,获取所有匹配的服务实例。解析结果 :将查询结果中的每个键值对的值部分(JSON 字符串)反序列化为 ServiceMetaInfo 对象。返回结果 :将所有解析后的 ServiceMetaInfo 对象收集到一个列表中并返回。异常处理 :确保在出现错误时能够适当处理,并提供有用的错误信息。
心跳检测和续期机制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @Override public void heartBeat() { // 10 秒续签一次 CronUtil.schedule("*/10 * * * * *", new Task() { @Override public void execute() { // 遍历本节点所有的 key for (String key : localRegisterNodeKeySet) { try { List<KeyValue> keyValues = kvClient.get(ByteSequence.from(key, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) .get() .getKvs(); // 该节点已过期(需要重启节点才能重新注册) if (CollUtil.isEmpty(keyValues)) { continue; } // 节点未过期,重新注册(相当于续签) KeyValue keyValue = keyValues.get(0); String value = keyValue.getValue().toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); ServiceMetaInfo serviceMetaInfo = JSONUtil.toBean(value, ServiceMetaInfo.class); register(serviceMetaInfo); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(key + "续签失败", e); } } } }); // 支持秒级别定时任务 CronUtil.setMatchSecond(true); CronUtil.start(); }
利用重新注册实现续签,定时任务是通过 CronUtil 类来完成的,来自于Hutool
服务节点下线
本地缓存,用一个列表来实现
自定义协议 自定义协议后TCP服务器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package com.yupi.yurpc.server.tcp; import com.yupi.yurpc.server.HttpServer; import io.vertx.core.Vertx; import io.vertx.core.buffer.Buffer; import io.vertx.core.net.NetServer; public class VertxTcpServer implements HttpServer { private byte[] handleRequest(byte[] requestData) { // 在这里编写处理请求的逻辑,根据 requestData 构造响应数据并返回 // 这里只是一个示例,实际逻辑需要根据具体的业务需求来实现 return "Hello, client!".getBytes(); } @Override public void doStart(int port) { // 创建 Vert.x 实例 Vertx vertx = Vertx.vertx(); // 创建 TCP 服务器 NetServer server = vertx.createNetServer(); // 处理请求 server.connectHandler(socket -> { // 处理连接 socket.handler(buffer -> { // 处理接收到的字节数组 byte[] requestData = buffer.getBytes(); // 在这里进行自定义的字节数组处理逻辑,比如解析请求、调用服务、构造响应等 byte[] responseData = handleRequest(requestData); // 发送响应 socket.write(Buffer.buffer(responseData)); }); }); // 启动 TCP 服务器并监听指定端口 server.listen(port, result -> { if (result.succeeded()) { System.out.println("TCP server started on port " + port); } else { System.err.println("Failed to start TCP server: " + result.cause()); } }); } public static void main(String[] args) { new VertxTcpServer().doStart(8888); } }
TCP客户端 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 package com.yupi.yurpc.server.tcp; import io.vertx.core.Vertx; public class VertxTcpClient { public void start() { // 创建 Vert.x 实例 Vertx vertx = Vertx.vertx(); vertx.createNetClient().connect(8888, "localhost", result -> { if (result.succeeded()) { System.out.println("Connected to TCP server"); io.vertx.core.net.NetSocket socket = result.result(); // 发送数据 socket.write("Hello, server!"); // 接收响应 socket.handler(buffer -> { System.out.println("Received response from server: " + buffer.toString()); }); } else { System.err.println("Failed to connect to TCP server"); } }); } public static void main(String[] args) { new VertxTcpClient().start(); } }
消息编码器与解码器
半包粘包
RecordParse的作用是:保证下次读到特定长度的字符。
负载均衡 轮询 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package com.yupi.yurpc.loadbalancer; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.ServiceMetaInfo; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * 轮询负载均衡器 * * @author <a href="https://github.com/liyupi">程序员鱼皮</a> * @learn <a href="https://codefather.cn">鱼皮的编程宝典</a> * @from <a href="https://yupi.icu">编程导航学习圈</a> */ public class RoundRobinLoadBalancer implements LoadBalancer { /** * 当前轮询的下标 */ private final AtomicInteger currentIndex = new AtomicInteger(0); @Override public ServiceMetaInfo select(Map<String, Object> requestParams, List<ServiceMetaInfo> serviceMetaInfoList) { if (serviceMetaInfoList.isEmpty()) { return null; } // 只有一个服务,无需轮询 int size = serviceMetaInfoList.size(); if (size == 1) { return serviceMetaInfoList.get(0); } // 取模算法轮询 int index = currentIndex.getAndIncrement() % size; return serviceMetaInfoList.get(index); } }
随机 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 // 只有 1 个服务,不用随机 if (size == 1) { return serviceMetaInfoList.get(0); } return serviceMetaInfoList.get(random.nextInt(size));
一致性Hash 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 package com.yupi.yurpc.loadbalancer; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.ServiceMetaInfo; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.TreeMap; /** * 一致性哈希负载均衡器 * * @author <a href="https://github.com/liyupi">程序员鱼皮</a> * @learn <a href="https://codefather.cn">鱼皮的编程宝典</a> * @from <a href="https://yupi.icu">编程导航学习圈</a> */ public class ConsistentHashLoadBalancer implements LoadBalancer { /** * 一致性 Hash 环,存放虚拟节点 */ private final TreeMap<Integer, ServiceMetaInfo> virtualNodes = new TreeMap<>(); /** * 虚拟节点数 */ private static final int VIRTUAL_NODE_NUM = 100; @Override public ServiceMetaInfo select(Map<String, Object> requestParams, List<ServiceMetaInfo> serviceMetaInfoList) { if (serviceMetaInfoList.isEmpty()) { return null; } // 构建虚拟节点环 for (ServiceMetaInfo serviceMetaInfo : serviceMetaInfoList) { for (int i = 0; i < VIRTUAL_NODE_NUM; i++) { int hash = getHash(serviceMetaInfo.getServiceAddress() + "#" + i); virtualNodes.put(hash, serviceMetaInfo); } } // 获取调用请求的 hash 值 int hash = getHash(requestParams); // 选择最接近且大于等于调用请求 hash 值的虚拟节点 Map.Entry<Integer, ServiceMetaInfo> entry = virtualNodes.ceilingEntry(hash); if (entry == null) { // 如果没有大于等于调用请求 hash 值的虚拟节点,则返回环首部的节点 entry = virtualNodes.firstEntry(); } return entry.getValue(); } /** * Hash 算法,可自行实现 * * @param key * @return */ private int getHash(Object key) { return key.hashCode(); } }
重试机制 不重试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package com.yupi.yurpc.fault.retry; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcResponse; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; /** * 不重试 - 重试策略 * * @author <a href="https://github.com/liyupi">程序员鱼皮</a> * @learn <a href="https://codefather.cn">鱼皮的编程宝典</a> * @from <a href="https://yupi.icu">编程导航学习圈</a> */ @Slf4j public class NoRetryStrategy implements RetryStrategy { /** * 重试 * * @param callable * @return * @throws Exception */ public RpcResponse doRetry(Callable<RpcResponse> callable) throws Exception { return callable.call(); } }
固定时间重试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 package com.yupi.yurpc.fault.retry; import com.github.rholder.retry.*; import com.yupi.yurpc.model.RpcResponse; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * 固定时间间隔 - 重试策略 * * @author <a href="https://github.com/liyupi">程序员鱼皮</a> * @learn <a href="https://codefather.cn">鱼皮的编程宝典</a> * @from <a href="https://yupi.icu">编程导航学习圈</a> */ @Slf4j public class FixedIntervalRetryStrategy implements RetryStrategy { /** * 重试 * * @param callable * @return * @throws ExecutionException * @throws RetryException */ public RpcResponse doRetry(Callable<RpcResponse> callable) throws ExecutionException, RetryException { Retryer<RpcResponse> retryer = RetryerBuilder.<RpcResponse>newBuilder() .retryIfExceptionOfType(Exception.class) .withWaitStrategy(WaitStrategies.fixedWait(3L, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .withStopStrategy(StopStrategies.stopAfterAttempt(3)) .withRetryListener(new RetryListener() { @Override public <V> void onRetry(Attempt<V> attempt) { log.info("重试次数 {}", attempt.getAttemptNumber()); } }) .build(); return retryer.call(callable); } }
容错机制